If you’re in a hurry: a deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance or tax benefit kicks in. Understanding deductible is essential whether it’s in health insurance, car coverage, or taxes — because it affects your payments, claims, and overall savings.
Many people wonder “what does deductible mean in health insurance?”, “what does tax deductible mean?”, or simply “what does deductible mean?”. Knowing the answer helps you plan for expenses, avoid surprises, and make smarter financial choices.
By the end of this guide, you’ll understand exactly what a deductible means, how it applies to different insurance types, coinsurance, tax deductions, and why terms like high deductible or annual deductible matter.
Definition & Meaning

A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket for covered expenses before your insurance company starts paying.
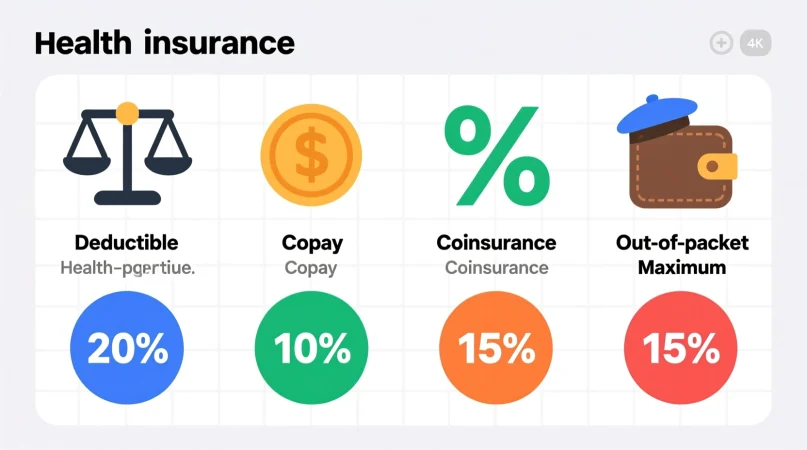
- Health Insurance: If your plan has a $1,000 deductible, you pay the first $1,000 of your medical bills. After that, insurance coverage begins.
- Car Insurance: If your deductible is $500 and you make a claim for $2,000 in damages, you pay $500, and your insurer covers the remaining $1,500.
- Taxes: A tax deductible expense reduces your taxable income. For example, charitable donations or mortgage interest can lower your taxes.
Dialogue Example:
A: “What does deductible mean in car insurance?”
B: “It’s the amount you pay yourself before the insurance covers the rest.”
Background & History
The term deductible originates from the concept of “deducting” from a total. In insurance, deductibles were introduced to prevent small or unnecessary claims, encouraging policyholders to share part of the cost.
In taxation, deductible expenses date back decades, allowing individuals and businesses to reduce taxable income for eligible expenses.
Today, the concept spans multiple areas: health, auto, home insurance, and tax deductions, making it a critical term for financial literacy.
Usage in Various Contexts
Health Insurance
- Annual Deductible: The total amount you must pay in a year before insurance coverage kicks in.
- High Deductible: Plans with higher out-of-pocket costs but lower premiums.
- Coinsurance after Deductible: After meeting your deductible, you may pay a percentage of the remaining costs.
Example:
A: “What does 50% coinsurance after deductible mean?”
B: “After paying your deductible, you cover 50% of costs, and insurance covers the rest.”
Car Insurance
- Deductible in Car Insurance: The out-of-pocket amount for repairs before coverage applies.
- Embedded Deductible: Applies individually to specific coverages within your policy.
Taxes
- Tax Deductible: Certain expenses, like mortgage interest or charitable contributions, reduce taxable income.
Dialogue Example:
A: “What does no deductible mean?”
B: “It means the insurer pays from the first dollar — you don’t pay anything out-of-pocket.”
Common Misconceptions & Clarifications
| Misconception | Reality |
|---|---|
| Deductible = premium | Premium is what you pay monthly; deductible is what you pay before coverage starts |
| Coinsurance covers everything | Coinsurance is a percentage you pay after meeting deductible |
| High deductible is bad | High deductible often means lower monthly premiums |
| Deductibles are the same across all insurances | Deductibles vary by plan type: health, auto, dental, etc. |
Similar Terms & Alternatives
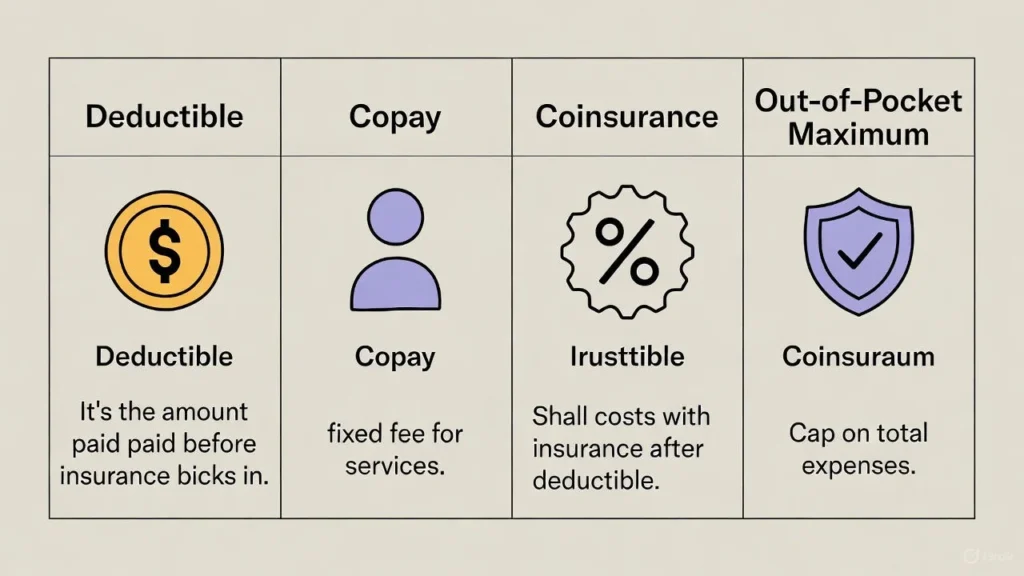
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The most you’ll pay in a year, including deductible and coinsurance.
- Copay: Fixed fee for services before or after deductible.
- Self-Insurance: Choosing to cover minor costs instead of using insurance.
How to Respond to Deductible-Related Queries

- Casual: “Oh, I’ve got a $500 deductible on that policy.”
- Professional: “The deductible is $1,000, which applies before coverage begins.”
- Informative: “After meeting your deductible, coinsurance applies for further claims.”
Regional or Cultural Differences

- U.S.: Standard in health, car, and home insurance policies.
- Other Countries: Deductible concepts exist but may differ in terminology or amount structure.
Comparison With Similar Terms
| Term | Context | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Deductible | Insurance, taxes | Out-of-pocket cost before coverage or benefit applies |
| Copay | Health services | Fixed payment per service |
| Coinsurance | Health, auto | Percentage of cost after deductible |
| Out-of-pocket maximum | Health/auto | Total limit of personal spending in a year |
Usage in Online Communities & Queries

People often search:
- “what does deductible mean in health insurance”
- “what does 20 after deductible mean”
- “what does 50 coinsurance after deductible mean”
Forums and blogs often explain deductibles with real-life scenarios to simplify confusing insurance terms.
Hidden or Misunderstood Meanings

- Deductible isn’t the same as a premium or total bill.
- Coinsurance percentages after deductible can be confusing.
- Tax deductible doesn’t mean free; it reduces taxable income, not total payment.
Suitability for Professional Communication

- Use “deductible” in financial planning, insurance policies, or tax discussions.
- For general audience explanations, add clarifying examples: “deductible is what you pay before insurance covers the rest.”
FAQs
1. What does deductible mean?
The amount you pay out-of-pocket before insurance or tax benefits apply.
2. What does deductible mean in health insurance?
It’s the money you pay before coverage begins; often paired with coinsurance.
3. What does tax deductible mean?
Expenses that reduce your taxable income, lowering your tax bill.
4. What does annual deductible mean?
The total deductible amount you must pay in a calendar year.
5. What does no charge after deductible mean?
After paying the deductible, insurance covers all remaining costs for that service.
6. What does 50% coinsurance after deductible mean?
You pay 50% of costs after the deductible, and insurance pays the other 50%.
7. What does high deductible mean?
A plan with higher out-of-pocket costs but usually lower monthly premiums.
Conclusion
Understanding what deductible mean is key for managing finances, insurance, and taxes.
If it’s health insurance, car insurance, or tax deductions, knowing your deductible, coinsurance, and out-of-pocket responsibilities ensures smart decisions and prevents surprises.
With this guide, you can confidently navigate insurance policies, tax benefits, and financial planning using deductibles wisely.

